Breast Reconstruction Surgery
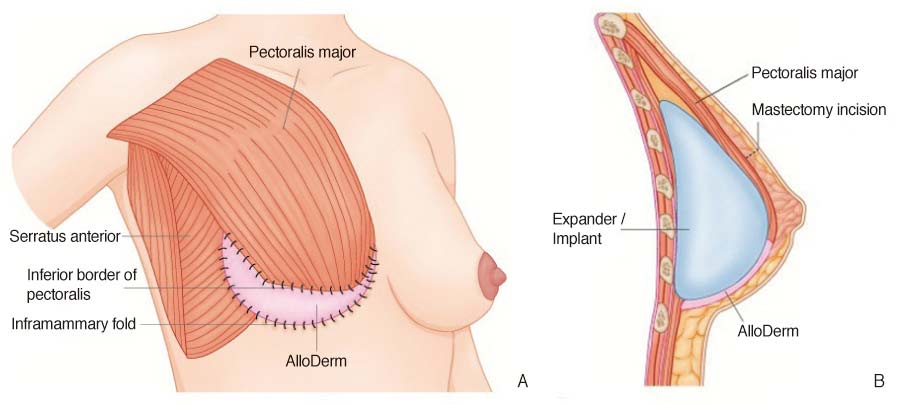
Breast reconstruction is the rebuilding of a breast, frequently in women. It requires using autologous tissue or prosthetic material to create a natural-looking breast, usually including the reformation of a natural-looking areola and nipple. This procedure requires the utilization of implants or tissue obtained from the rest of the woman’s body.
Typically, the aesthetic appearance is acceptable to the girl; nevertheless, the reconstructed place is typically entirely numb afterward, resulting in loss of sexual function and the ability to perceive pain due to burns and other injuries.
The principal area of the procedure may often be moved out immediately after the mastectomy. Just like many other surgeries, patients with substantial medical comorbidities (high body stress, obesity, diabetes) and smokers are higher-risk candidates. Surgeons may possibly choose to do postponed reconstruction to reduce that risk. There is little evidence accessible from randomized reports to favor immediate or postponed reconstruction. The infection rate might be higher with principal reconstruction (done at the same time frame as mastectomy).
Still, you will find psychological and financial advantages to presenting a single primary reconstruction. Patients expected to get radiation therapy included in their adjuvant treatment will also be typically considered for postponed autologous reconstruction due to considerably higher complication costs with tissue expander-implant techniques in these patients. Waiting for half a year to per year following may possibly reduce the danger of complications, but that risk will always be higher in patients who’ve obtained radiation therapy.

Delayed breast reconstruction is considered more challenging than immediate reconstruction. Frequently not merely breast volume but also skin surface place must be restored. Several patients starting delayed breast reconstruction have now been formerly treated with radiation or experienced a reconstruction disappointment with immediate breast reconstruction. In nearly all cases of delayed breast reconstruction, tissue must certainly be lent from yet another area of the human body to really make the new breast.
Breast reconstruction is a big undertaking that usually takes numerous operations. Often these follow-up surgeries are disseminated over months or months. If an implant can be used, the average person has precisely the same risks and complications as people who utilize them for breast augmentation but has higher costs of capsular contracture (tightening or hardening of the scar tissue across the implant) and revisional surgeries.
